The Essential Guide to Balanced Nutrition for Lifelong Health
Introduction
Proper nutrition forms the foundation of good health, yet many struggle to maintain a balanced diet in today’s fast-paced world. This comprehensive guide explores the core principles of healthy eating, debunks common nutrition myths, and provides practical strategies for making sustainable dietary changes. Whether you’re looking to boost energy levels, manage weight, or prevent chronic disease, understanding these nutritional fundamentals will set you on the path to optimal wellbeing.
Understanding Macronutrients
The three primary macronutrients each play unique roles in maintaining bodily functions:
Carbohydrates
Often misunderstood, quality carbohydrates serve as the body’s preferred energy source. Focus on:
- Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice
- Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables
- Legumes and starchy vegetables
Proteins
Essential for tissue repair and immune function, proteins should come from diverse sources:
- Lean animal proteins (fish, poultry)
- Plant-based options (lentils, tempeh, edamame)
- Dairy or dairy alternatives
Fats
Healthy fats support brain function and hormone production:
- Monounsaturated fats (avocados, olive oil)
- Omega-3 fatty acids (fatty fish, walnuts)
- Limit processed trans fats
Micronutrients Matter
Vitamins and minerals work synergistically to support hundreds of biochemical processes:
Key Vitamins
- Vitamin D: Crucial for bone health and immunity
- B Vitamins: Support energy metabolism
- Vitamin C: Powerful antioxidant and collagen booster
Essential Minerals
- Magnesium: Involved in over 300 enzyme reactions
- Iron: Oxygen transport and energy production
- Zinc: Immune support and wound healing
Hydration Fundamentals
Water comprises about 60% of our body weight and is involved in nearly every physiological process:
Hydration Tips
- Start your day with a glass of water
- Infuse water with fruits or herbs for flavor
- Monitor urine color (pale yellow indicates proper hydration)
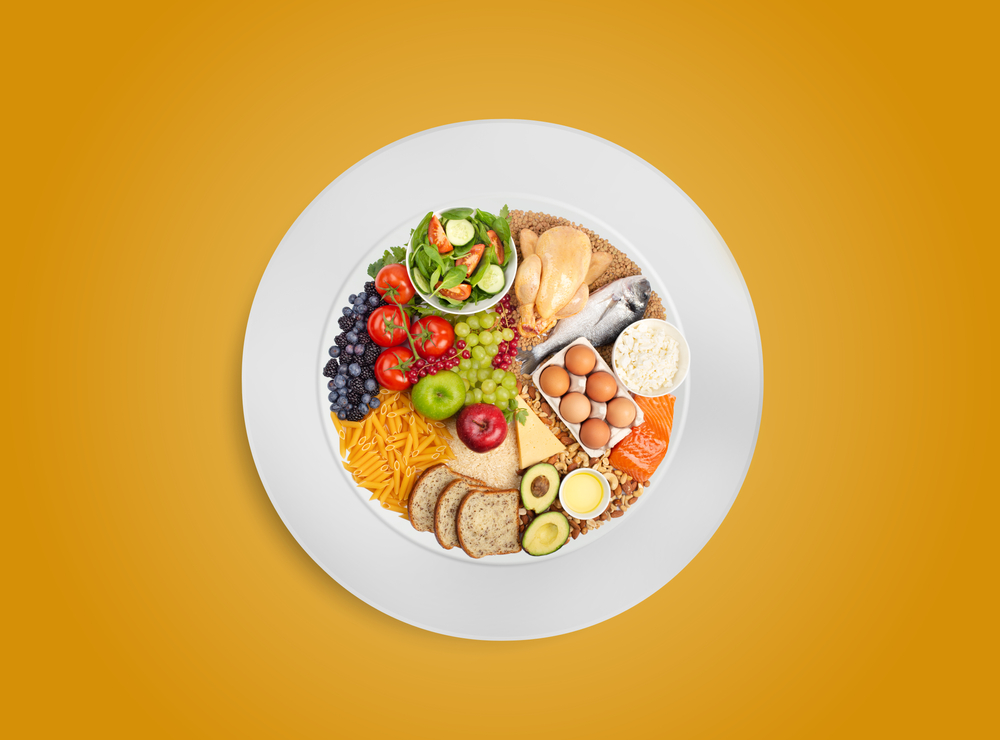
Building a Balanced Plate
The Harvard Healthy Eating Plate provides an excellent visual guide:
Vegetables and Fruits
- Fill half your plate with colorful varieties
- Aim for seasonal, locally-grown options when possible
Whole Grains
- Choose minimally processed options
- Examples: farro, whole wheat, oats
Protein Sources
- Vary between plant and animal sources
- Include fatty fish twice weekly
Healthy Fats
- Use oils for cooking and dressings
- Incorporate nuts and seeds
Common Nutrition Myths Debunked
Myth: All calories are equal
Truth: Food quality matters more than calorie counting. 100 calories of vegetables affects your body differently than 100 calories of candy.
Myth: Fat makes you fat
Truth: Healthy fats promote satiety and support metabolism.
Myth: You need to detox regularly
Truth: Your liver and kidneys naturally detoxify your body.
Practical Eating Strategies
Meal Planning Basics
- Prepare staples in bulk (grains, roasted vegetables)
- Keep healthy snacks readily available
- Use the “plate method” for balanced meals
Smart Grocery Shopping
- Shop the perimeter for fresh foods
- Read nutrition labels carefully
- Choose frozen fruits/vegetables when fresh isn’t available
Dining Out Tips
- Request dressings/sauces on the side
- Start with a vegetable-based appetizer
- Practice mindful eating
Special Considerations
Nutrition Through Life Stages
- Children: Focus on growth and development
- Adults: Maintain health and prevent disease
- Seniors: Address changing nutritional needs
Dietary Restrictions
- Gluten-free: Naturally gluten-free whole foods
- Dairy-free: Calcium-rich alternatives
- Vegetarian/Vegan: Protein combining strategies
Making Lasting Changes
Setting Realistic Goals
- Start with small, manageable changes
- Focus on adding healthy foods rather than restriction
Overcoming Challenges
- Plan for busy days
- Find healthy alternatives to cravings
- Practice self-compassion
Conclusion
Optimal nutrition doesn’t require perfection, but rather consistent, mindful choices. By focusing on whole, minimally processed foods and listening to your body’s signals, you can develop eating habits that support lifelong health. Remember that progress matters more than perfection – each healthy choice contributes to your wellbeing.
Next Steps
- Identify one nutritional change to implement this week
- Experiment with new healthy recipes
- Consult a registered dietitian for personalized advice
This science-backed guide provides the foundation for making informed nutritional choices. By understanding these principles and applying them consistently, you’ll be well on your way to achieving and maintaining optimal health through proper nutrition.